“One package to fuse them all.”— The Lord of the Rings (probably)
A high‑performance, Rust‑accelerated toolkit for multi‑modality cardiac image fusion and registration ﮩ٨ـﮩﮩ٨ـ♡ﮩ٨ـﮩﮩ٨ـ.
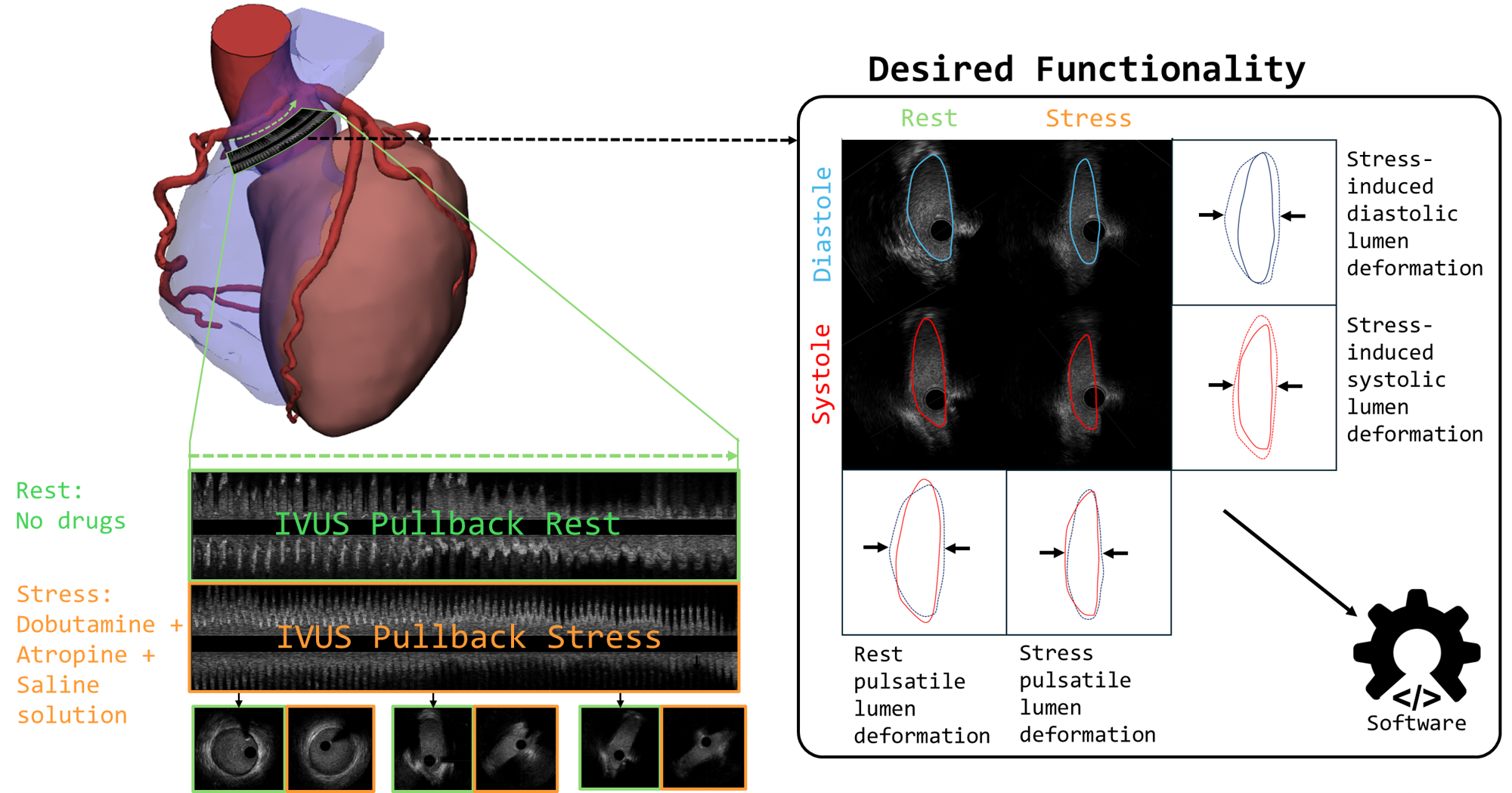
multimoda-rs is a high-performance toolkit developed to enable the study of dynamic vessel deformation in coronary artery anomalies (CAAs), where quantifying lumen changes under stress and rest is critical. It addresses the general challenge of aligning and fusing diverse cardiac imaging modalities, such as CCTA, IVUS, OCT, and MRI—into a unified, high‑resolution 3D model. While CCTA provides comprehensive volumetric context, intravascular modalities (IVUS and OCT) offer sub‑millimeter resolution along the vessel lumen, and MRI (LGE) reveals tissue characteristics like scar and edema. This library leverages Rust for computationally intensive registration steps, delivering faster performance than pure Python implementations.
- IVUS/OCT Contours Registration
- Aligns pullback sequences (rest vs. stress, diastole vs. systole) using Hausdorff distance on vessel contours and catheter centroids.
- Supports four alignment modes:
- Full: register all four phases (rest‑dia, rest‑sys, stress‑dia, stress‑sys)
- Double-pair: two pairs (rest vs. stress).
- Single-pair: diastole vs. systole.
- Single: one phase only.
- Centerline Alignment
- Align registered geometries onto a vessel centerline using three‑point or manual rotation methods.
- Geometry Utilities
- Smooth contours, reorder frames to minimize spatial and index jumps, compute areas and elliptic ratios, find farthest/closest point pairs, and more.
Either directly from PyPI (recommended):
pip install multimodarsor by cloning the repo and building the project yourself:
# Install rust in case you don't have it on your system
curl --proto '=https' --tlsv1.2 -sSf https://sh.rustup.rs | sh
git clone https://github.com/yungselm/multimoda-rs.git
python -m venv .venv
source .venv/bin/activate
pip install maturin
. "$HOME/.cargo/env" # Set rust env
maturin developNote: In case you get the following error:
💥 maturin failed
Caused by: rustc, the rust compiler, is not installed or not in PATH. This package requires Rust and Cargo to compile extensions. Install it through the system's package manager or via https://rustup.rs/.
execute the following commands:
unset -v VIRTUAL_ENV
maturin develop
Run the script with the provided test cases, to ensure sufficient set up.
import multimodars as mm
import numpy as np
# IVUS pullbacks: full alignment of rest/stress & diastole/systole
rest, stress, dia, sys, _ = mm.from_file(
mode="full",
rest_input_path="data/ivus_rest",
stress_input_path="data/ivus_stress"
)
# Load raw centerline
cl_raw = np.genfromtxt("data/centerline_raw.csv", delimiter=",")
centerline = mm.numpy_to_centerline(cl_raw)
# Align geometry pair onto centerline
aligned_pair, cl_resampled = mm.to_centerline(
mode="three_pt",
centerline=centerline,
geometry_pair=rest, # e.g. Rest geometry (dia/sys)
aortic_ref_pt=(12.26, -201.36, 1751.06),
upper_ref_pt=(11.76, -202.19, 1754.80),
lower_ref_pt=(15.66, -202.19, 1749.97)
)
# Optionally save aligned to obj
mm.to_obj(aligned_pair.dia_geom, "data/aligned.obj")
mm.centerline_to_obj(cl_resampled, "data/resampled_cl.obj")For detailed signatures and usage examples, see the online documentation. The intended usage of the package with examples for every case are provided under examples with Jupyter Notebooks to follow along.
Distributed under the MIT License. See LICENSE for details.
This package was initially built to study anomalous aortic origin of a coronary artery (AAOCA). In these patients, a dynamic stenosis is present where the intramural section (inside the aortic wall) undergoes complex lumen deformation:
-
Pulsatile deformation during rest and stress with every heartbeat (diastole vs. systole).
-
Stress-induced deformation from rest to stress for both diastole and systole.
The from_file() and from_array() functions and their processing modes (full, double-pair, etc.) were specifically designed to quantify these four distinct geometric states, which are crucial for diagnosis and treatment planning.
While inspired by CAAs, multimoda-rs is a general-purpose toolkit for multi-modality cardiac image fusion.
-
Intravascular Imaging (IVUS/OCT) + CCTA: While coronary computed tomography angiography (CCTA) is the gold standard for 3D anatomic information, intravascular imaging (intravascular ultrasound (IVUS) and optical coherence tomography (OCT)) offers a much higher resolution. This package enables the replacement of sections of the CCTA-derived coronary artery model with these high-resolution intravascular images. Since intravascular images are acquired during a catheter pullback and the vessel undergoes motion (heartbeat, breathing), the images within a pullback are not perfectly aligned. This package first registers these images to each other using Hausdorff distances of the vessel contours and the catheter centroid position. The Rust backend leverages parallelization to achieve significantly faster results than pure Python.
-
Longitudinal Studies (Pre-/Post-Stenting): The same registration functionality is directly applicable to longitudinal comparisons in coronary artery disease, such as assessing the results of percutaneous coronary intervention (comparing pre-stent vs. post-stent pullbacks).
The options to display are therefore:
full
`Rest`: `Stress`:
diastole ----------------------> diastole
| |
| |
v v
systole ----------------------> systole
double pair
`Rest`: `Stress`:
diastole diastole
| |
| |
v v
systole systole
single pair
`Rest`/`Stress`:
diastole
|
|
v
systole
single
diastole rest / systole rest / diastole stress / systole stress
The expected input data for contours is the following for a csv file:
Expected format .csv file, e.g.:
--------------------------------------------------------------------
| 185 | 5.32 | 2.37 | 0.0 |
| ... | ... | ... | ... |
No headers -> frame index, x-coord [mm], y-coord [mm], z-coord [mm]
The contours can also be in pixels, but results of the .get_area() function will be wrong.
The output allows for the creation of several interpolated meshes. These can then be used to render videos displaying the dynamics.
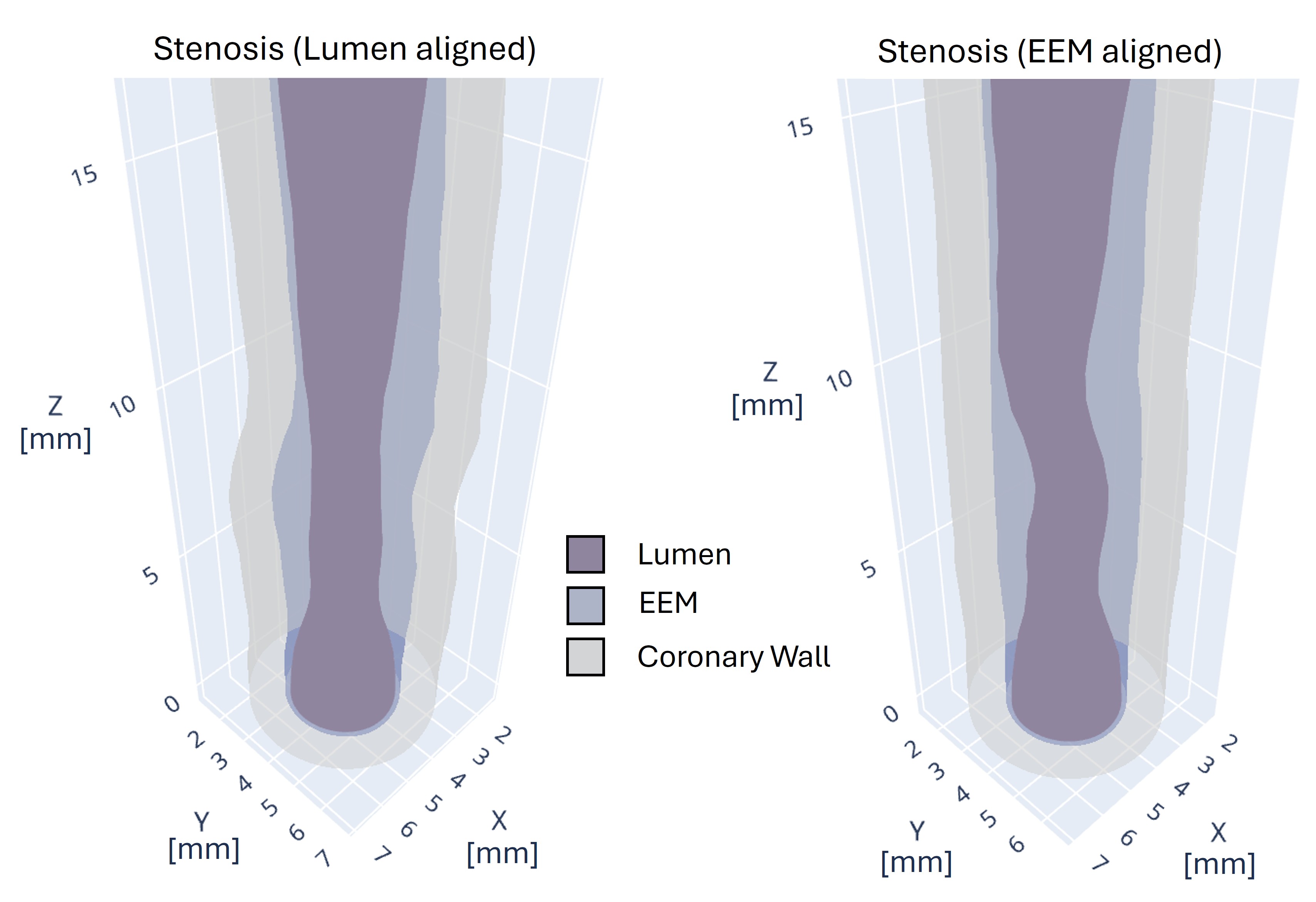
The package works in the same way for other clinical applications such as pre- and post-stent alignment (An example is provided in data/ivus_prestent and data/ivus_poststent) or for coronary artery disease. Here it is also possible to read in contour information for e.g. lumen, external elastic membrane and create a coronary wall (See figure).
The data for this example is provided under data/ivus_full.
OCT registration works exactly the same as IVUS registration, just the parameters for image resolution have to be set differently.
Please kindly cite the following paper if you use this repository.
@article{stark2025multimodars,
title = {multimodars: A Rust-powered toolkit for multi-modality cardiac image fusion and registration},
author = {Stark, Anselm W. and Ilic, Marc and Mokhtari, Ali and Mohammadi Kazaj, Pooya and Graeni, Christoph and Shiri, Isaac},
journal = {arXiv preprint arXiv:2510.06241},
year = {2025}
}
Stark, Anselm W., Marc Ilic, Ali Mokhtari, Pooya Mohammadi Kazaj, Christoph Graeni, and Isaac Shiri. "multimodars: A Rust-powered toolkit for multi-modality cardiac image fusion and registration." arXiv preprint arXiv:2510.06241 (2025).